大约 2 分钟
注意
推荐环境:Centos7,文档环境:Centos7
文件结构
脚本文件名
脚本的命名一般为 文件名.sh 扩展名为 sh(sh代表shell),扩展名并不影响脚本执行,可要可不要,只是为了能直接区分是否为脚本文件
脚本内容
第一行一般为 #!/bin/bash,#! 是一个约定的标记,它告诉系统这个脚本需要什么解释器来执行,即使用哪一种 Shell,必须写。
后面为注释或者脚本命令,以#开头的行就是注释,会被解释器忽略。
语法结构
shell脚本传递变量
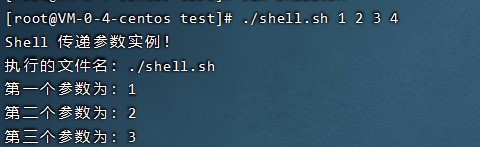
在执行 Shell 脚本时,向脚本传递参数,脚本内获取参数的格式为:$n。n 代表一个数字,1 为执行脚本的第一个参数,2 为执行脚本的第二个参数,以此类推。
脚本示例如下:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Shell 传递参数实例!";
echo "执行的文件名:$0";
echo "第一个参数为:$1";
echo "第二个参数为:$2";
echo "第三个参数为:$3";
执行结果如下
shell脚本流程控制
if语句
if condition
then
command1
command2
...
commandN
fi
if else 语句
if condition
then
command1
command2
...
commandN
else
command
fi
case语句
case 值 in
模式1)
command1
command2
...
commandN
;;
模式2)
command1
command2
...
commandN
;;
esac
实例
以下是包含传递参数、if、case语句的脚本文件
APP_NAME=/root/item.jar
#使用说明,用来提示输入参数
usage() {
echo "Usage: sh item.sh [start|stop|restart|status]"
exit 1
}
#检查程序是否在运行
is_exist(){
pid=111
#如果不存在返回1,存在返回0
if [ -z "${pid}" ]; then
return 1
else
return 0
fi
}
#启动方法
start(){
echo "${APP_NAME} is starting. pid=${pid}"
}
#停止方法
stop(){
is_exist
#判断上一条指定的返回值是否等于0
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
echo "${APP_NAME} is stopping"
else
echo "${APP_NAME} is not running"
fi
}
#输出运行状态
status(){
is_exist
#判断上一条指定的返回值是否等于0
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
echo "${APP_NAME} is running. Pid is ${pid}"
else
echo "${APP_NAME} is NOT running."
fi
}
#重启
restart(){
stop
sleep 5
start
}
#根据输入参数,选择执行对应方法,不输入则执行使用说明
case "$1" in
"start")
start
;;
"stop")
stop
;;
"status")
status
;;
"restart")
restart
;;
*)
usage
;;
esac
以下是统一清理业务应用日志文件的shell文件。
#!bin/bash
rm -rf /var/log/myapp.log
rm -rf /home/app/apache-tomcat/logs/*.log
rm -rf /home/app/apache-tomcat/logs/*.out
echo 'clean over~'